5.1.1 Tinnitus, Hyperacusis and Neural Plasticity
What is tinnitus?

Ringing in the ears. Tinnitus is a phantom noise perception, caused by repeated, habitual firing of auditory neurons.
Tinnitus is a condition where a phantom ringing or buzzing noise is heard inside the ear or the head. It is the name of a symptom and could have many causes.
Acute or extended noise exposure is the most common cause in an estimated 80% of tinnitus cases. Other causes include stress, head injury, toxicity from chemical exposures or drugs, damage from infections viruses, or surgery, or occasionally acoustic neuroma—a tumour on the auditory nerve. If tinnitus is in one ear only, it is normal to test for acoustic neuroma.
Tinnitus often accompanies hearing loss but neither causes the other. It often accompanies blocked ear or Eustachian tube problems or other types of ear malfunction.
Tinnitus caused by noise is generally associated with cilia damage in the inner ear. However, the process of tinnitus occurs in the brain, not the ear, due to repetitive firing of neurons, usually following some type damage to the ear mechanism.

How does Sound Therapy help tinnitus?

Sound Therapy remaps the auditory brain pathways to normalize sound perception.
It helps to restore normal function of the whole hearing system.
Neural plasticity and Sound Therapy
Neural stimulus (high frequency sound) builds new brain pathways. Establishing correct auditory pathways can help to improve hearing perception and reduce or eliminate tinnitus.
This means that Sound Therapy helps to calm hyper active brain cells, which can be another cause of tinnitus.
Also recommend colloidal minerals and powerful anti oxidants as noise causes free radical damage to the inner ear. We call this Nutrition for the Ear. More information on these supplements is available via the links on our website.
Neural Plasticity and Sound Therapy
In the last twenty to fifty years, neural plasticity has been scientifically proven. This means that new brain pathways can be created if the brain is given the right stimulus. (Doidge.) High frequency, varied, complex and meaningful sound is an effective way to build new neural pathways in the auditory centres.
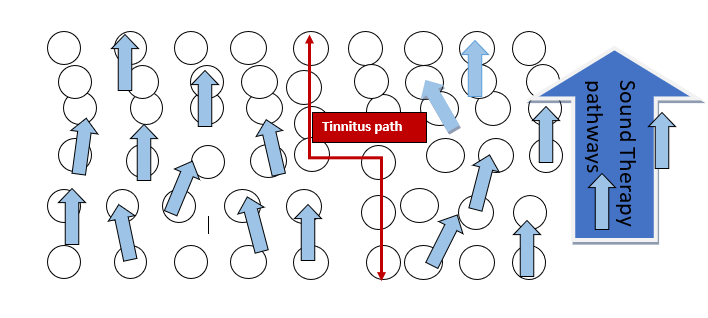
Tinnitus pathways
In chronic tinnitus, set pathways in the brain fire repeatedly, creating the experience of tinnitus noise. Initially this firing pattern is the result of damage to some part of the auditory system, whether the ear drum, middle ear, inner ear or auditory nerves. Such damage may be caused by noise, infection, toxicity or injury. The damage interferes with the normal transmission of correct sound to the brain. As a result, the brain may create a compensatory signal, which is tinnitus.
(Jastreboff.)
Creating new pathways with Sound Therapy
Sound Therapy music is designed to create varied, meaningful, complex broad spectrum auditory stimulation, with a particular emphasis on high frequency sounds. High frequency sound instinctively carries a strong emotional importance. The rich complexity and structure of classical music engages many parts of the brain. Therefore, this type of sound grabs the attention, activating numerous brain centres, and is very effective in creating new, alternate pathways for sound transmission. The more new brain pathways are created, the better the chance that the tinnitus pathways will stop dominating the attention and ultimately perhaps stop firing entirely.
What is hyperacusis?

Sound Therapy reduces sound sensitivity by normalizing ear and brain responses to sound.
We believe that Sound Therapy alleviates hyperacusis by remapping brain pathways and reducing hyperactive neural firing, as well as restoring normal function to the ear itself. In effect, it restores the ability of the auditory system to moderate the volume of sounds that reach the brain.
The program gently activates all parts of the ear with the aim of restoring the ear’s natural ability to protect itself from noise that is too loud, as well as improving the perception of all frequencies of sound.

